Art, Design, and Color Basics
|
Fundamentals of Design (slides) | GCFLearnFree.org
|
Principles of Design
Elements of Art
|
Color Basics
App
|
|
Video Lecture
Basics of Adobe Illustrator
Illustrator Basics |
Drawing Tools |
Using Color |
Still need help? Check out the Adobe Illustrator User Guide.
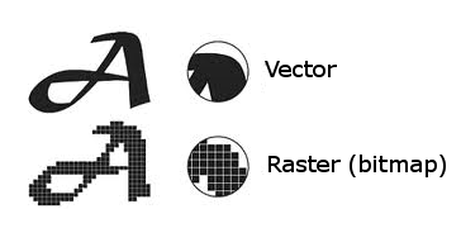
Raster vs. Vector
|
In computer graphics there are two types of images: Raster (aka. bitmap) and Vector. Raster images are based on a grid of pixels while vector images are based on a mathematical grid with paths that align to the grid making them resolution independent.
|
|
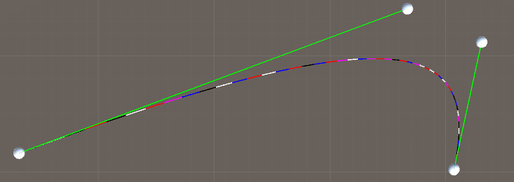
A Key Component of Vector Graphics are Bézier Curves
The ability to draw using Bézier curves is an integral part of creating vector illustration. These mathematical curves were first developed in 1959 by Paul de Casteljau. Later, Étienne Bézier— a French engineer—popularized the Bézier Curve.
Further Exploration
Artists |
Reading |
|
Terminology
- Aesthetics - the branch of philosophy dealing with such notions as the beautiful,the ugly, the sublime, the comic, etc., as applicable to the fine arts,with a view to establishing the meaning and validity of criticaljudgments concerning works of art, and the principles underlying orjustifying such judgments.
- Bézier curve - a curved line or path defined by mathematical equations.
- Color - The visual sensation dependent on the reflection or absorption of light from a given surface. The three characteristics of colors are hue, intensity, and value.
- Color Relationships - Also called color schemes or harmonies. The relationships of colors on the color wheel. Basic color schemes include:
- Monochromatic - Monochromatic color is any set of colors that all have the same hue with different levels of white tinting and black shading
- Analogous - Analogous colors are colors that sit next to each other on a color wheel that have a similar hue such as red and violet.
- Complementary - Complementary colors are two colors that are on opposite sides of the color wheel. When next to each other appear brighter but when mixed create effective neutral hues which are great for shadows.
- Color Wheel - A circular diagram of the spectrum used to show the relationships between the colors
- Composition - The overall placement and organization of elements in a work of art, as well as the interrelationships between individual elements.
- Design - The plan, conception or organization of a work of art; the arrangement of independent parts (the elements of art) to form a coordinated whole.
- Hue - Name of the color.
- Media/Medium - Referring to materials used to make works of art. Classifications of artworks, such as painting, printmaking, sculpture, film, etc.).
- Negative Space - Shapes or spaces that are or represent the areas unoccupied by objects.
- Principles of Design - A design concept describing the ways in which the elements of an image are arranged (i.e. balance, contrast, dominance, emphasis, movement, repetition, rhythm, variation, unity).
- Positive Space - Shapes or spaces in an image that represent solid objects or forms.
- Technique - The manner and skill in which an artist uses tools and materials to achieve an expressive effect.
- Unity - A principle of design that connects a variety of elements of art and principles of design into a work of art with harmony and balance.
- Variety - A principle of art concerned with combining one or more elements of art in different ways to create interest.
- Vector - In digital art, art composed of mathematical lines, curves, and paths.